Foam Rolling: Bona Fide or Passing Fad?

Ten years ago you’d be hard pressed to find a selection of foam rollers at your local gym. A two-foot-round piece of blue foam might have left some athletes, coaches and physiotherapists scratching their heads wondering exactly what it was to be used for.
Today, nearly every elite level training facility, physio clinic, and neighbourhood gym contains an array of foam rollers in varying lengths and consistencies. The question is, is foam rolling a legitimate therapeutic technique or a flash-in-the-pan?
What is a foam roller and how is it used?
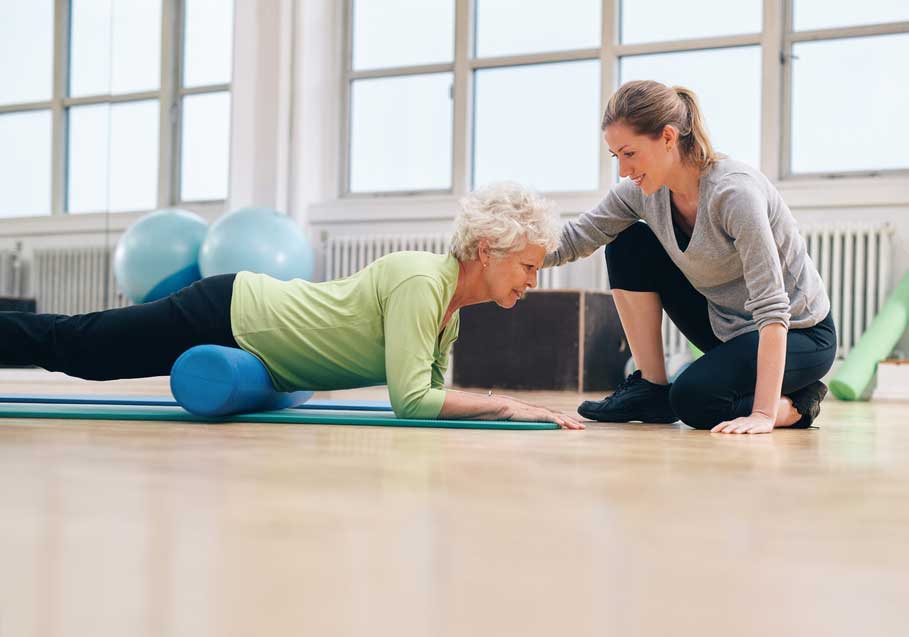
A foam roller is a cylindrical piece of hard-celled foam, available in a range of shapes and sizes, that can be used as a self-massage tool. Athletes, gym-goers or patients can use a roller to administer pressure to sensitive areas in the muscles – whether it’s applying sweeping strokes to the long muscle groups like the calves, adductors and quadriceps or concentrating minute directed force to areas like the hip rotators, gluteus medius and tensor fascia latae, the muscle that attaches to the IT Band. Your therapist or trainer may call these sore areas “knots,” “trigger points,” or simply areas of increased muscle density. Regardless of the name, those in the fields of athletics and rehabilitation know that in order to improve performance, sore muscles need massaging.
What started the foam roller craze?
For years chiropractors and physical therapists working with elite athletes have focused on injury prevention and the treatment of muscles by using soft tissue mobilization (massage) and muscle activation and release techniques. Results spoke for themselves and soon it was mandatory that professional athletes have a team of muscle manipulators in their corner. Of course, not everyone is a professional athlete, or can afford a personal trainer, so the question arose: “How can I benefit from soft tissue massage at a reasonable cost?” Enter Mike Clark, physical therapist and CEO of the National Academy of Sports Medicine in the USA. He is credited by many for introducing the athletic and physical therapy communities to the foam roller and what he termed “self myofascial release.” Simply put, he convinced the masses to “self massage” by getting a foam roller and using your bodyweight to apply pressure to sore spots.
What are the major muscle areas that respond well to foam rolling?
• Gluteus Maximus and Hip Rotators: sitting on the roller with a slight tilt and moving from the iliac crest to the hip joint, addresses the gluteus maximus muscles. To concentrate on the hip rotators, the affected leg is crossed to place the hip rotator group on stretch.
• Tensor Fascia Latae and Gluteus Medius: Although small, these muscles are significant factors when experiencing anterior knee pain. To address the TFL, begin with the body prone and the edge of the roller placed over the TFL, just below the iliac crest. After working the TFL, turn ninety degrees to a side position and work from the hip joint to the iliac crest to address the gluteus medius.
• Adductors: the adductors are one of the most neglected areas of the lower body. The easiest method for working the adductors is a floor-based technique where you abduct the leg over the roller and place the roller at about a 60 degree angle to the leg. The rolling action should be done in three portions beginning just above the knee in the area of the vastus medialis and pes anserine. Ten short rolls should be done covering about one third the length of the femur. Next the roller should be moved to the mid-point of the adductor group and again rolled ten times in the middle third of the muscle. Lastly, the roller should be moved high into the groin, almost to the pubic symphysis.
Things to remember
-
Foam rolling can be hard work, particularly for weaker or overweight people, as the arms are heavily involved in moving the body.
-
Rolling can border on painful at first. If you feel a “sharp” or knife-like pain, however, stop immediately. Rest and then try again with lighter pressure.
-
Foam rollers are available in a number of densities from relatively soft foam, (slightly harder than a pool noodle), to newer high-density rollers with a much more solid feel.
-
The feel of the roller and the intensity of the self-massage work must be properly geared to the age, and fitness level of the client.
-
Good massage work, and correspondingly good self-massage work, may be uncomfortable, much like stretching.
-
It is important that you learn to distinguish between a moderate level of discomfort related to a trigger point and a potentially injurious situation.
-
Foam rolling should be used with discretion in those clients with less muscle density. And it should never cause bruising.
-
The reality is that you should feel better, not worse after using a foam roller.
If you have tight, sore muscles after your hike or workout, you might want to explore what a foam roller can do for you. They’re a small investment (prices start at $20) but can potentially decrease the number of soft tissue injuries one experiences.
Alternatively, join us at Mountain Trek where our staff will show you how to utilize a foam roller properly and set you on a path to overall wellness.
[fbcomments]
 How often have you said to yourself, “This summer I’m going to take better care of myself. I’m going to eat healthier, exercise, swim and get outside more!” But then the work piles up, weddings and other celebrations happen complete with beer and barbecues, the kids need your undivided attention, the weather doesn’t cooperate and before you know it, summer’s over and you’re feeling even worse than you did before it started.
How often have you said to yourself, “This summer I’m going to take better care of myself. I’m going to eat healthier, exercise, swim and get outside more!” But then the work piles up, weddings and other celebrations happen complete with beer and barbecues, the kids need your undivided attention, the weather doesn’t cooperate and before you know it, summer’s over and you’re feeling even worse than you did before it started. Helping you to rekindle the desire to move your body (through our vitalizing daily hikes), lower stress, improve sleep, lengthen and strengthen muscles, and balance blood sugars, is all part of Mountain Trek’s Prevention Program to reboot metabolism and balance hormones.
Helping you to rekindle the desire to move your body (through our vitalizing daily hikes), lower stress, improve sleep, lengthen and strengthen muscles, and balance blood sugars, is all part of Mountain Trek’s Prevention Program to reboot metabolism and balance hormones. August is the month for recreation, relaxation and retreat. You’ve worked hard all year and now you deserve to take some time for yourself: it’s time to leave behind the stresses and worries of your job, or whatever it is that occupies too much of your time, if even for a little while. Whether you need to do this on your own, or you’re happy to have your spouse, family or friends join you, it’s time to treat yourself to a Mountain Trek experience! And that experience just got stepped up a notch…
August is the month for recreation, relaxation and retreat. You’ve worked hard all year and now you deserve to take some time for yourself: it’s time to leave behind the stresses and worries of your job, or whatever it is that occupies too much of your time, if even for a little while. Whether you need to do this on your own, or you’re happy to have your spouse, family or friends join you, it’s time to treat yourself to a Mountain Trek experience! And that experience just got stepped up a notch… Cooking Re-Mastered with Chef Laurie Hartland
Cooking Re-Mastered with Chef Laurie Hartland




 What better way to see out the old, and ring in the New Year than walking on top of the snow, breathing fresh air in a winter wonderland, while melting off inches from holiday indulgence?
What better way to see out the old, and ring in the New Year than walking on top of the snow, breathing fresh air in a winter wonderland, while melting off inches from holiday indulgence?

