Summer Salad Dressings
It’s time to put more life into your salads. Spruce them up with these two delicious Mountain Trek dressings.
We all need food to survive but to live well and free of disease eating the right type of food is necessary.
It’s time to put more life into your salads. Spruce them up with these two delicious Mountain Trek dressings.

Jenna and Rob at Fry Creek on a Thursday, the 5th day of the Mountain Trek program, when they were feeling “great,” “light,” and “energized.”
Recently we asked two visitors who attended Mountain Trek Health Retreat in B.C. to document their daily revelations, pains, challenges, and successes. Each was given the same list of questions over the six-day program and their responses are an excellent snapshot of how people change throughout the week.
The reasons we chose to feature Jenna and Rob are they’re relatively close in age, they both lead busy lives in Vancouver (they hadn’t met before), they’re at similar fitness levels and they both came to Mountain Trek to “destress” and “rejuvenate” in a beautiful setting. Jenna is a hard-working partner at a marketing and Web development studio and Rob is a writer and musician whose lifestyle can get a little “Rock’nRoll” at times.
Below are honest accounts of their experiences, in their own words. Sum up how you feel right now in 20 words or less.
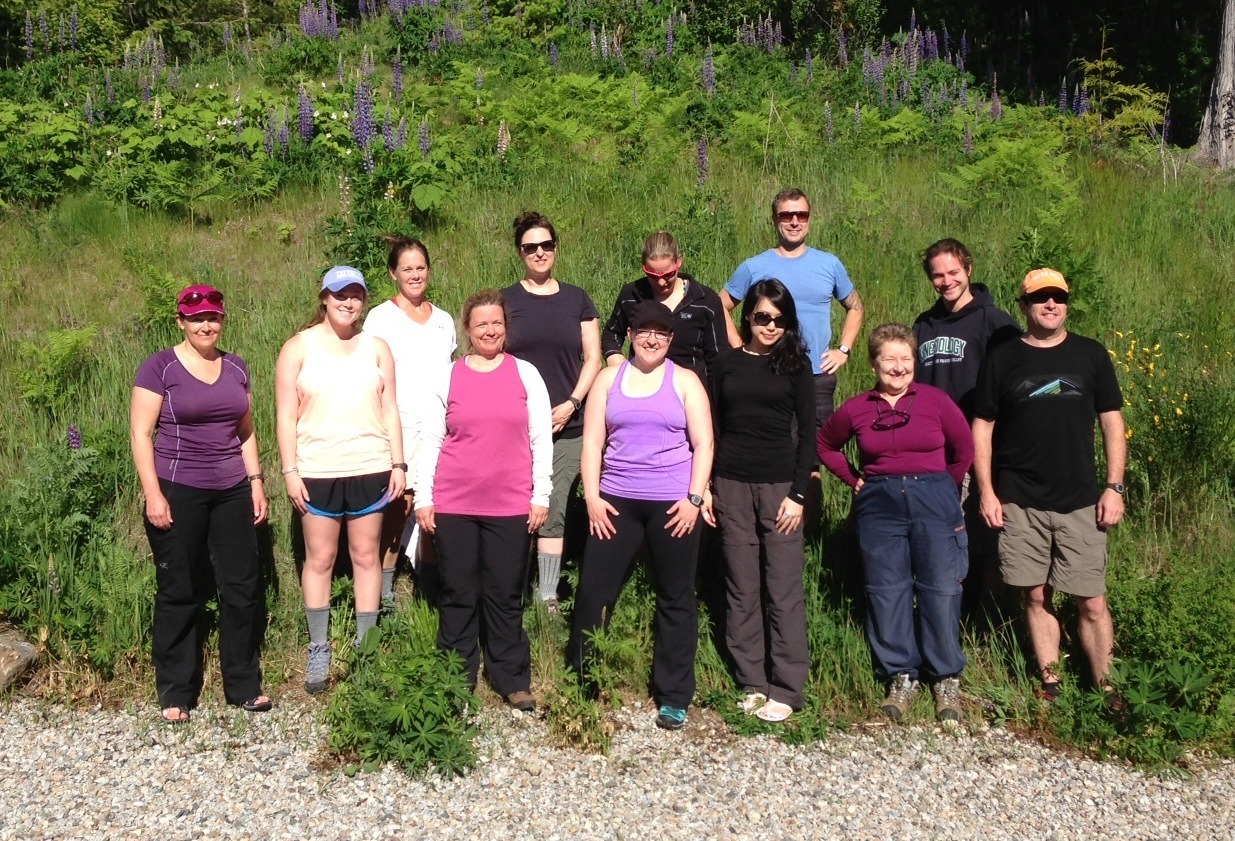

Jenna and Rob are in the back row of this group shot. Rob’s wearing blue. Jenna is in black.
Mountain Trek is the health reset you’ve been looking for. Our award-winning retreat, immersed in the lush nature of British Columbia, will help you unplug, recharge, and roll back years of stress and unhealthy habits. To learn more about the retreat, and how we can help you reset your health, please email us at info@mountaintrek.com or reach out below:

The group on the trip to Machu Picchu, Peru, last Spring. Phil Lanni is the second from left.
Welcome to the second installment of our Q&A series, which features guests who have visited Mountain Trek. Each person came to our fitness retreat for their own reasons and they all had different experiences. Last time we spoke with Debra Fordham, who’s visit to Mountain Trek last year was the catalyst for a 70-pound weight loss. In this piece we speak with Philip Lanni, a business owner living near Toronto, Ontario, who is “three-quarters retired” he says. He’s visited Mountain Trek every year since 2002 and he’s also joined us on a few of our global adventures including the hike to Everest base camp and this year’s trek to Macchu Piccu. Phil makes the journey to Mountain Trek every year because, “I like the adrenaline of pushing myself.” Pretty inspiring for a man who’s celebrating his 65th birthday this year. Here is Phil’s story.
Hi Phil. Thank you so much for agreeing to speak with us. Firstly, how did you find out about Mountain Trek?
On the internet. I’d done a lot of hiking before in the States but I wanted to find something in Canada. That was in 2002. And I’ve been coming back every year since. I brought my wife a few times and my kids. I also brought along my brother and my brother-in-law because they were both experiencing some health issues at the time. They all got something out of their visit.
Tell us about your expectations?
When I was 35, I smoked 70 cigarettes a day and was around 275 pounds. I had three small kids then and I knew I had to make some changes. I started eating better, walking and doing more healthy things and eventually got down to 230 pounds on my own. That was 30 years ago and since then I’ve attended many different resorts but they’re not in the same league as Mountain Trek in terms of what you get for you money…it may be a bit more expensive than other retreats but you really do get what you pay for.
What are some of the highlights of your time at Mountain Trek?
I like the adrenaline of pushing myself to the point where I feel I just can’t go any further – and then I do. I love that I’m competing against myself rather than anyone else. I find that really invigorating. To be able to do that in the kind of scenery Mountain Trek is located in, well, you just can’t replace it. Another highlight is the staff. They’re so great because they live the life. They walk the talk, which makes the program a lot easier to accept because they’re living proof that it works. And finally, I never did yoga before and Mountain Trek got me into it, which is great. I find as you get older, yoga definitely helps you to be more flexible.
What’s a “lowlight” from your experiences at Mountain Trek?
I once sprained my foot and wasn’t able to participate in the rest of the hikes that week. But even though I couldn’t go hiking I still managed to lose seven pounds just eating the food!

Phil and the crew in Peru
For me Mountain Trek is just a continuation of my routine. I do two hours of exercise a day to stay healthy. Then, I’ll go to the lodge and maybe I’ll lose five or six pounds (the same I lose every time) but it’s just part of my routine now. I probably eat a little more when I come home because of going out to restaurants and things.
So what draws you back to Mountain Trek every year, Phil?
Again, it’s just part of my routine. I use it as a basis to steer my life in the right direction. Going to Mountain Trek helps me maintain a weight of around 200 pounds and 18% body fat. (Ed note: According to the Jackson & Pollock Body Fat Percentage Chart, 20% body fat is “ideal” for someone over 56 years of age. Phil is exceeding that.)
What would be your advice to someone who is thinking about coming to Mountain Trek?
Be prepared to get rid of your inhibitions. Some people say, “Oh I won’t be able to keep up with the rest” but it’s not about that. You’re not competing against anyone but yourself. It’s all about getting rid of your demons…It’s about your total health, not just weight loss.
Anything else you want to tell our readers about the Mountain Trek experience?
The yoga instructors, coaches and guides, they’re all excellent. And the quality of food is very good. I never get hungry when I’m there!

Concerns of heart disease, obesity, and diabetes are on the rise. People are rethinking their nutrition and the types of liquids they consume. It’s no secret that drinking too much soda is not good for your body, but why should you choose water over Coca-Cola and Pepsi?
The two companies have engaged in many different marketing campaigns, and today they own some of the most recognizable brands on the planet. In fact, 1.8 billion bottles of Coke are consumed around the world every day! Both Coca-Cola and Pepsi have made efforts by introducing no-sugar, no-calorie beverage options, but these diet versions still have harmful effects.
The fact is, no matter how these products are advertised they will never come close to the health benefits of water.
Mountain Trek is the health reset you’ve been looking for. Our award-winning health retreat, immersed in the lush nature of British Columbia, will help you detox, unplug, recharge, and roll back years of stress and unhealthy habits. To learn more about the retreat, and how we can help you reset your health, please email us at info@mountaintrek.com or reach out below:
At Mountain Trek we know how important it is to have help staying on track during our hectic lives. We regularly hear from our alumni that they love staying in touch with the other guests they met while at the resort and that this support network is key to integrating healthy habits in their day-t0-day.
But sometimes we need more than just a friendly phone call to help us with our health or weight-loss goals. This is when new technology comes in handy. Below are five of the best health-related mobile apps that we’ve come across. Do you have other suggestions for us? If so, please comment below.
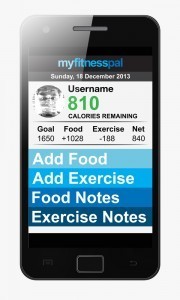 FitnessPal Calorie Counter and Diet Tracker
FitnessPal Calorie Counter and Diet TrackerFitPal is one of the most popular apps on the market, and not just because it’s free. Users can set a daily calorie goal, then record food intake and exercise to help stay on track. The app records your meals and workouts, then automatically calculates the number of calories consumed. And it’s food database is extensive with caloric and nutritional details of over 425,000 foods. It includes:
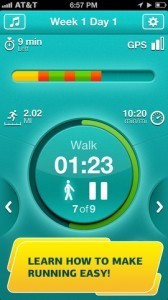 WalkJogRun
WalkJogRunWalkJogRun is an online community of runners, walkers and hikers sharing routes and encouragement with one another. It uses your smart phone’s GPS technology to pinpoint your current location and then suggests routes that have been uploaded by other users. From there you can plot a course, record your own route and at the end of your run you can check distance, pace, time, etc. The $4.99 version includes:
This app is a little more hardcore than what we’d normally suggest but we really like the yoga and stretches component. Six Pack App offers multiple exercises and routines for the chest, shoulders, back, legs and, of course, abs. One of the best parts of the app is the “Don’t” section which shows you things not to do while performing the exercise, thus ensuring you maintain good form and avoid injury. Get the $0.99 version to avoid all the pop-up ads. Features include:
 Nike Training Club
Nike Training ClubNike’s most popular training app is called NTC and it’s billed as “your personal trainer, anytime, anywhere.” While it lacks the personality of say, someone like Mountain Trek’s head guide Kirkland Shave, it does have more than 100 custom-built workouts as well as those used by celebrities Serena Williams and Paula Radcliffe. For a free app, NTC is very robust and it does a lot including:
 Calm
Calm
Feeling in the mood for mexican but want to skip all those heavy burritos and cheese dishes. Try our non-alcoholic Sangria.

Welcome to the first of our Q&A series, which features guests who have visited Mountain Trek. Each came to our fitness retreat for their own reasons and they all had different experiences. In this inaugural piece we speak with Debra Fordham, a television writer living in Los Angeles, California, who visited Mountain Trek for a week in May 2012. Since that time she has lost almost 70 pounds and is training to run a half-marathon again. This is Debra’s story.
Debra Fordham (second from left) on her visit to Mountain Trek.
I was feeling low one day and sitting at the computer googling generic topics like “fitness retreats” and “weight loss” when the Mountain Trek link popped up. I checked out the Trip Advisor comments and most of them included the words “life changing.” It struck me as a bit expensive so I called my friend to ask advice. She said, “How much would you spend to change your life?” I booked the next day.
Well, I went in 80 pounds overweight and out of shape. Honestly, I wasn’t expecting it to be as hard as it was. I knew we’d get good food and go on hikes but I was surprised by the raw physical challenge and the evening lessons regarding healthy living. That said, the experience literally did change my life. After six days of eating healthy foods, exercising and detoxing my entire physiology changed. When I got home I no longer craved soda or Oreos.
I wanted to buy a house in the Kootenay region. It’s just so beautiful there. I also really enjoyed Kirkland’s lectures in the evening – they gave me not only an understanding of what I was going through in terms of physiology but I was also given tools to use when I returned home.
I wanted to physically give up at one point. I was thinking of myself as this fat girl who doesn’t exercise and it was all too much but the wonderful thing is the staff wouldn’t let me give up – they just inspired me to keep going. I was amazed at how motivated I was around the guides, most especially Kirkland, Cathy and Krista.
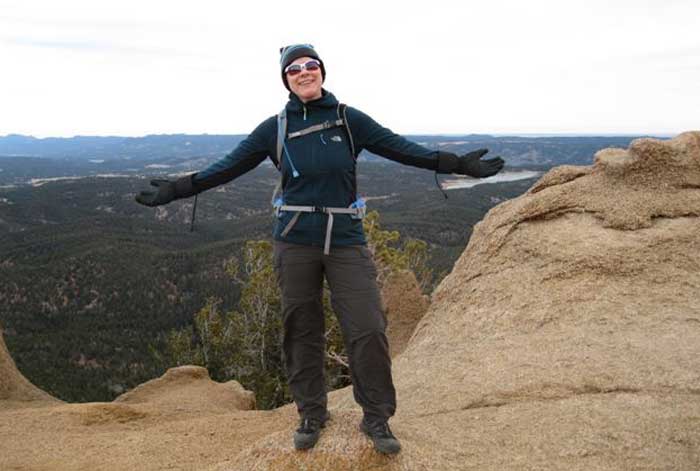

Debra, over 50 pounds lighter
When I got home I craved healthy foods. I also craved exercise and I continued hiking around my area. And I acted on Kirk’s lectures – I started cooking for myself. I made bliss balls and Mt Trek soups and I stopped eating processed food.
I was doing really well until the holidays when I got together with my family. We have such a wacked idea of food – we eat like crazy. I had people at my house at Christmas and so we started baking and because of the family dynamics – well, you just don’t want to eat tofu salad while someone you love is eating something unhealthy. It’s kind of a social statement not joining in.
Mountain Trek staff kept stressing “Have more good days than bad” and that really is the key. Sometimes you just have to eat the snacks on the airplane and it’s important you not beat yourself up about it. I don’t let it derail me. I’ll enjoy a “no limits” great meal but the next morning I’m back on the pony eating foods from the local farmer’s market.
Go!!!! With five exclamation points! For some people it may seem expensive but like my friend says, “How much would you pay to change your life?” You have to take it seriously – you’ll be challenged but it really will be the launching pad to changing your life.
I can’t wait to come back! I’m coordinating with someone who I met there last May and we’re going to return together. That was another benefit of the experience – the alumni are an amazing resource and they become your friends.
[fbcomments]
Ok, you’ve made some lifestyle changes, drink more water, eat more salad, go for a walk a few times a week…so why does that last 20 lbs of weight hang on so stubbornly? It’s great you’ve made those changes, but there could be a few factors that thwart your health and weight loss goals:
If you take a long view of your health, you can gradually make changes that stick. If you are pressed for time, with risks to your heart or impending diabetes, you might need to make changes quickly.
Mountain Trek is the health reset you’ve been looking for. Our award-winning health retreat, immersed in the lush nature of British Columbia and featuring daily sunrise yoga and night-time restorative yoga, will help you unplug, recharge, and roll back years of stress, anxiety, and unhealthy habits. To learn more about the retreat, and how we can help you reset your health, please email us at info@mountaintrek.com or reach out below: